link : http://www.opengl-tutorial.org/kr/intermediate-tutorials/tutorial-12-opengl-extensions/
12번째 튜토리얼 시작!
Extensions
새로운 세대마다 GPU의 성능이 향상되어 더 많은 삼각형과 더 많은 픽셀을 렌더링 할 수 있습니다.
하지만, 원시 성능만이 유일한 관심사는 아니다.
NVIDIA, AMD 및 Intel은 더 많은 기능을 제공함으로써 그래픽 카드를 향상시킵니다. 몇 가지 예를 살펴보겠다.
ARB_fragment_program
2002년에는 GPU에 정점 셰이더나 조각 셰이더가 없고, 모든 것이 칩 내부에 하드 코드되었습니다.
이를 Fixed-Function Pipeline (FFP)라고 한다.
따라서 OpenGL 1.3인 API의 최신 버전은 존재하지 않았기 때문에 소위 "셰이더"를 생성, 조작 및 사용할 수 있는 방법이 없었다.
그러나 NVIDIA는 수백 개의 플래그 및 상태 변수 대신 실제 코드로 렌더링 프로세스를 설명하는 것이 편리할 수 있다고 판단했다.
이것은 ARB_fragment_program이 생성된 방법이다. GLSL이 없지만 대신 다음과 같이 작성할 수 있다.
!!ARBfp1.0 MOV result.color, fragment.color; END하지만 분명히 OpenGL에 이러한 코드를 사용하도록 지시하려면 OpenGL에 아직 없는 특수 기능이 필요하다.
설명으로 넘어 가기 전에 한 가지 더 예를 들어보겠다.
ARB_debug_output
ARB_fragment_program은 너무 오래되어서 더 이상 필요하지 않다. 편리한 새로운 확장 기능이 ARB_debug_output에 존재한다.
OpenGL 3.3에는 존재하지 않지만 어쨌든 사용할 수 있는 기능을 제공한다. GL_DEBUG_OUTPUT_SYNCHRONOUS_ARB 또는
GL_DEBUG_SEVERITY_MEDIUM_ARB와 같은 토큰과 DebugMessageCallbackARB와 같은 토큰을 정의한다.
이 확장 기능의 가장 큰 장점은 잘못된 코드를 작성할 때마다 다음과 같은 이점이 있다는 것이다.
glEnable(GL_TEXTURE); // Incorrect ! You probably meant GL_TEXTURE_2D !오류 메시지와 문제점의 정확한 위치를 알 수 있다.
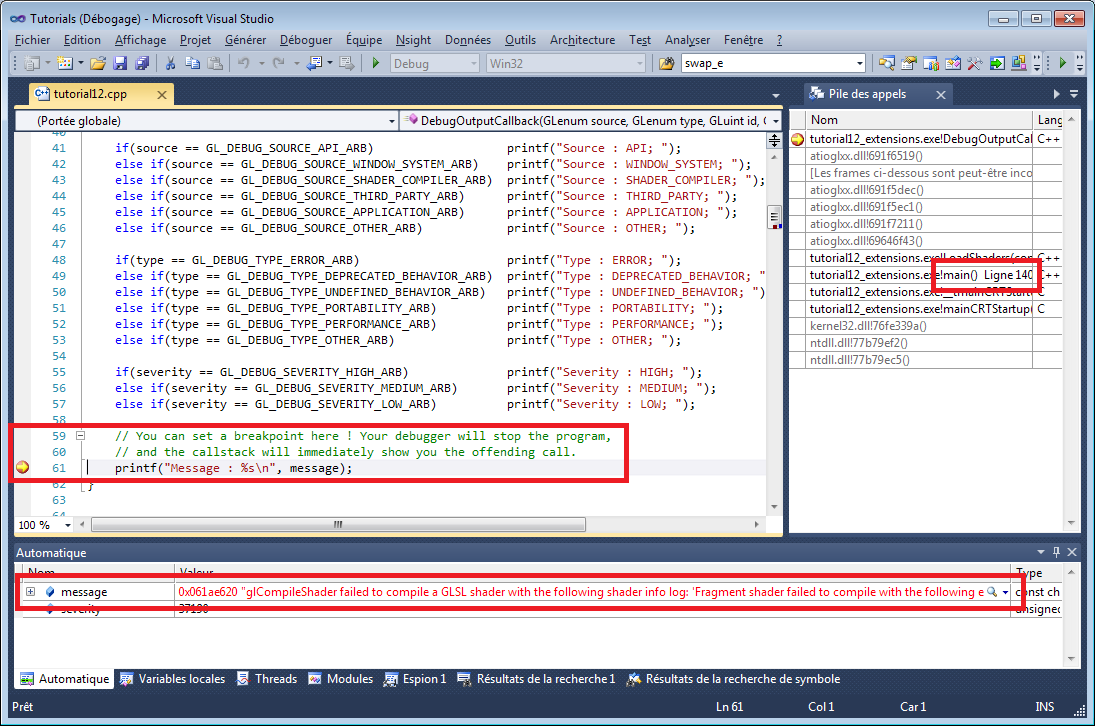
Getting an extension - the hard way
검사를 위한 "manual" 방법은 OpenGL.org wiki에서 이 코드 스니펫을 사용하는 것이다.
int NumberOfExtensions;
glGetIntegerv(GL_NUM_EXTENSIONS, &NumberOfExtensions);
for(i=0; i<NumberOfExtensions; i++) {
const GLubyte *ccc=glGetStringi(GL_EXTENSIONS, i);
if ( strcmp(ccc, (const GLubyte *)"GL_ARB_debug_output") == 0 ){
// The extension is supported by our hardware and driver
// Try to get the "glDebugMessageCallbackARB" function :
glDebugMessageCallbackARB = (PFNGLDEBUGMESSAGECALLBACKARBPROC) wglGetProcAddress("glDebugMessageCallbackARB");
}
}Getting all extensions - the easy way
이 모든 것은 매우 복잡하다. GLEW, GLee, gl3w 등의 라이브러리는 훨씬 쉽게 만든다. 예를 들어 GLEW를 사용하면
창을 만든 후에 glewinit()을 호출하면 유용한 변수가 만들어진다.
if (GLEW_ARB_debug_output){ // Ta-Dah ! }(주의 : debug_output은 컨텍스트 생성시 활성화해야하기 때문에 특별하다.
GLFW에서는 glfwOpenWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_DEBUG_CONTEXT,1);)로 수행된다.
ARB vs EXT vs ...
각 확장의 이름에는 가용성에 대한 정보가 들어있다.
GL_ : 모든 플랫폼
GLX_ : Linux 및 Mac 전용 (X11)
WGL_ : Windows 전용
EXT : 일반적인 확장자
ARB : OpenGL Architecture Review Board의 모든 구성원이 확장을 허용함
Designing with Extentions
The problem
OpenGL 3.3 응용 프로그램에서 큰 선을 렌더링해야 한다고 가정해보겠다. 이를 위해 복잡한 버텍스 쉐이더를 작성하거나
GL_NV_path_rendering을 사용하면 모든 복잡한 작업을 처리할 수 있다.
따라서 다음과 같은 코드가 생성된다.
if ( GLEW_NV_path_rendering ){
glPathStringNV( ... ); // Draw the shape. Easy !
}else{
// Else what ? You still have to draw the lines
// on older NVIDIA hardware, on AMD and on INTEL !
// So you have to implement it yourself anyway !
}Choosing the limit
렌더링 품질 또는 성능의 향상이 두 가지 다른 경로를 유지하는 데 따른 고통보다 중요 할 때 일반적으로 확장을 사용하도록 선택한다.
예를 들어, Braid(시간을 여행하는 2D게임)에는 이전 하드웨어에서 렌더링되지 않았던 시간을 낭비할 때 모든 종류의 이미지 왜곡 효과가 있었다.
OpenGL 3.3 이상에서는 당신이 필요한 99% 이상의 도구가 있다. 일부 확장은 GL_AMD_pinned_memory와 같이 매우 유용하지만,
GL_ARB_framebuffer_object(used for Render To Texture)를 사용하면 게임을 10배나 더 잘 보이게 할 수 있는 몇 년전과 같지 않은 경우가 많다.
그래도 오래된 하드웨어를 처리해야한다면 OpenGL 3+를 사용할 수 없으므로 OpenGL 2+를 사용해야한다.
Conclusion
OpenGL Extentions는 사용자의 GPU에 따라 OpenGL의 기능을 확장하는 좋은 방법을 제공한다.
대부분의 기능이 이미 핵심이기 때문에 확장 기능은 대부분 고급 사용을 위한 것이지만, 기능이 어떻게 작동하는지 그리고
소프트웨어를 개선하는데 사용할 수 있는 방법을 아는 것은 중요하다!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 692 693 694 695 696 697 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716 717 718 719 720 721 722 723 724 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 750 751 752 753 754 755 756 757 758 759 760 761 762 763 764 765 766 767 768 769 770 771 772 773 774 775 776 777 778 779 780 781 782 783 784 785 786 787 788 789 790 791 792 793 794 795 796 797 798 799 800 801 802 803 804 805 806 807 808 809 810 811 812 813 814 815 816 817 818 819 820 821 822 823 824 825 826 827 828 829 830 831 832 833 834 835 836 837 838 839 840 841 842 843 844 845 846 847 848 849 850 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 863 864 865 866 867 868 869 870 871 872 873 874 875 876 877 878 879 880 881 882 883 884 885 886 887 888 889 890 891 892 893 894 895 896 897 898 899 900 901 902 903 904 905 906 907 908 909 910 911 912 913 914 915 916 917 918 919 920 921 922 923 924 925 926 927 928 929 930 931 932 933 | #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <sstream> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <GL/glew.h> #include <glfw3.h> #include <GL/glew.h> GLFWwindow* window; #include <glm/glm.hpp> #include <glm/gtx/transform.hpp> using namespace glm; #define FOURCC_DXT1 0x31545844 // Equivalent to "DXT1" in ASCII #define FOURCC_DXT3 0x33545844 // Equivalent to "DXT3" in ASCII #define FOURCC_DXT5 0x35545844 // Equivalent to "DXT5" in ASCII GLuint LoadShaders(const char *, const char *); GLuint loadBMP_custom(const char *); GLuint loadDDS(const char *); bool loadOBJ( const char *, std::vector<glm::vec3> &, std::vector<glm::vec2> &, std::vector<glm::vec3> &); void indexVBO( std::vector<glm::vec3> & , std::vector<glm::vec2> & , std::vector<glm::vec3> & , std::vector<unsigned short> & , std::vector<glm::vec3> & , std::vector<glm::vec2> & , std::vector<glm::vec3> & ); //mouse-keyboard input void computeMatricesFromInputs(); glm::mat4 getViewMatrix(); glm::mat4 getProjectionMatrix(); glm::mat4 ViewMatrix; glm::mat4 ProjectionMatrix; glm::mat4 getViewMatrix() { return ViewMatrix; } glm::mat4 getProjectionMatrix() { return ProjectionMatrix; } struct PackedVertex { glm::vec3 position; glm::vec2 uv; glm::vec3 normal; bool operator<(const PackedVertex that) const { return memcmp((void*)this, (void*)&that, sizeof(PackedVertex))>0; }; }; bool getSimilarVertexIndex_fast( PackedVertex & packed, std::map<PackedVertex, unsigned short> & VertexToOutIndex, unsigned short & result ) { std::map<PackedVertex, unsigned short>::iterator it = VertexToOutIndex.find(packed); if (it == VertexToOutIndex.end()) { return false; } else { result = it->second; return true; } } //text2D unsigned int Text2DTextureID; unsigned int Text2DVertexBufferID; unsigned int Text2DUVBufferID; unsigned int Text2DShaderID; unsigned int Text2DUniformID; void initText2D(const char *); void printText2D(const char *, int, int, int); void cleanupText2D(); //포지션 초기화 glm::vec3 position = glm::vec3(0, 0, 5); float horizontalAngle = 3.14f; float verticalAngle = 0.0f; float initialFoV = 45.0f; float speed = 3.0f; float mouseSpeed = 0.005f; void APIENTRY DebugOutputCallback(GLenum source, GLenum type, GLuint id, GLenum severity, GLsizei length, const GLchar* message, const void* userParam) { printf("OpenGL Debug Output message : "); if (source == GL_DEBUG_SOURCE_API_ARB) printf("Source : API; "); else if (source == GL_DEBUG_SOURCE_WINDOW_SYSTEM_ARB) printf("Source : WINDOW_SYSTEM; "); else if (source == GL_DEBUG_SOURCE_SHADER_COMPILER_ARB) printf("Source : SHADER_COMPILER; "); else if (source == GL_DEBUG_SOURCE_THIRD_PARTY_ARB) printf("Source : THIRD_PARTY; "); else if (source == GL_DEBUG_SOURCE_APPLICATION_ARB) printf("Source : APPLICATION; "); else if (source == GL_DEBUG_SOURCE_OTHER_ARB) printf("Source : OTHER; "); if (type == GL_DEBUG_TYPE_ERROR_ARB) printf("Type : ERROR; "); else if (type == GL_DEBUG_TYPE_DEPRECATED_BEHAVIOR_ARB) printf("Type : DEPRECATED_BEHAVIOR; "); else if (type == GL_DEBUG_TYPE_UNDEFINED_BEHAVIOR_ARB) printf("Type : UNDEFINED_BEHAVIOR; "); else if (type == GL_DEBUG_TYPE_PORTABILITY_ARB) printf("Type : PORTABILITY; "); else if (type == GL_DEBUG_TYPE_PERFORMANCE_ARB) printf("Type : PERFORMANCE; "); else if (type == GL_DEBUG_TYPE_OTHER_ARB) printf("Type : OTHER; "); if (severity == GL_DEBUG_SEVERITY_HIGH_ARB) printf("Severity : HIGH; "); else if (severity == GL_DEBUG_SEVERITY_MEDIUM_ARB) printf("Severity : MEDIUM; "); else if (severity == GL_DEBUG_SEVERITY_LOW_ARB) printf("Severity : LOW; "); //break point를 여기에 설정해라, 당신의 디버거는 프로그램을 멈출 것이다 //callstack은 바로 너에게 offending call을 보여줄 것이다 printf("Mesage : %s\n", message); } int main() { // Initialise GLFW if (!glfwInit()) { fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize GLFW\n"); getchar(); return -1; } glfwWindowHint(GLFW_SAMPLES, 4); glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3); glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3); glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE); // To make MacOS happy; should not be needed glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE); // Open a window and create its OpenGL context window = glfwCreateWindow(1024, 768, "QBOT_opengl", NULL, NULL); if (window == NULL) { fprintf(stderr, "Failed to open GLFW window. If you have an Intel GPU, they are not 3.3 compatible. Try the 2.1 version of the tutorials.\n"); getchar(); glfwTerminate(); return -1; } glfwMakeContextCurrent(window); // Initialize GLEW glewExperimental = true; if (glewInit() != GLEW_OK) { fprintf(stderr, "Failed to initialize GLEW\n"); getchar(); glfwTerminate(); return -1; } // Example 1: if (GLEW_AMD_seamless_cubemap_per_texture) { printf("The GL_AMD_seamless_cubemap_per_texture is present, (but we're not goint to use it)\n"); //이제 glTexParameterf를 TEXTURE_CUBE_MAP_SEAMLESS_ARB 매개 변수와 함께 호출하는 것이 합법적이다 //분명히 이 코드는 AMD가 아닌 하드웨어에서는 실표할 것이기 때문에 테스트해야한다 } // Example 2: if (GLEW_ARB_debug_output) { printf("The OpenGL implementation provides debug output. Let's use it!\n"); glDebugMessageCallbackARB(&DebugOutputCallback, NULL); glEnable(GL_DEBUG_OUTPUT_SYNCHRONOUS_ARB); } else { printf("ARB_debug_output unavailable. You have to use glGetError() and/or gDebugger to catch mistakes.\n"); } // Ensure we can capture the escape key being pressed below glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_STICKY_KEYS, GL_TRUE); glfwSetInputMode(window, GLFW_CURSOR, GLFW_CURSOR_DISABLED); // Set the mouse at the center of the screen glfwPollEvents(); glfwSetCursorPos(window, 1024 / 2, 768 / 2); // Dark blue background glClearColor(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.4f, 0.0f); glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST); glDepthFunc(GL_LESS); glEnable(GL_CULL_FACE); GLuint VertexArrayID; glGenVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID); glBindVertexArray(VertexArrayID); //Shader를 불러온다. GLuint programID = LoadShaders("StandardShading.vertexshader", "StandardShading.fragmentshader"); //매트릭스ID 추가 GLuint MatrixID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "MVP"); GLuint ViewMatrixID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "V"); GLuint ModelMatrixID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "M"); //어떠한 두 가지의 함수를 사용해서 텍스처를 불러온다 //GLuint Texture = loadBMP_custom("uvtemplate.bmp"); GLuint Texture = loadDDS("uvmap.DDS"); GLuint TextureID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "myTextureSampler"); //우리의 .obj file을 읽는다 std::vector<glm::vec3> vertices; std::vector<glm::vec2> uvs; std::vector<glm::vec3> normals; bool res = loadOBJ("suzanne.obj", vertices, uvs, normals); std::vector<unsigned short> indices; std::vector<glm::vec3> indexed_vertices; std::vector<glm::vec2> indexed_uvs; std::vector<glm::vec3> indexed_normals; indexVBO(vertices, uvs, normals, indices, indexed_vertices, indexed_uvs, indexed_normals); GLuint vertexbuffer; glGenBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexed_vertices.size() * sizeof(glm::vec3), &indexed_vertices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); GLuint uvbuffer; glGenBuffers(1, &uvbuffer); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, uvbuffer); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexed_uvs.size() * sizeof(glm::vec2), &indexed_uvs[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); GLuint normalbuffer; glGenBuffers(1, &normalbuffer); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, normalbuffer); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexed_normals.size() * sizeof(glm::vec3), &indexed_normals[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); // Generate a buffer for the indices as well GLuint elementbuffer; glGenBuffers(1, &elementbuffer); glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, elementbuffer); glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indices.size() * sizeof(unsigned short), &indices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); glUseProgram(programID); GLuint LightID = glGetUniformLocation(programID, "LightPosition_worldspace"); //little text library를 초기화 initText2D("Holstein.DDS"); //speed computation double lastTime = glfwGetTime(); int nbFrames = 0; //enable blending glEnable(GL_BLEND); glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA); do { //속도 측정 double currentTime = glfwGetTime(); nbFrames++; if (currentTime - lastTime >= 1.0) { printf("%f ms/frame\n", 1000.0 / double(nbFrames)); nbFrames = 0; lastTime += 1.0; } // Clear the screen. It's not mentioned before Tutorial 02, but it can cause flickering, so it's there nonetheless. glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); glUseProgram(programID); //키보드와 마우스 인풋으로부터의 MVP 매트릭스를 계산한다 computeMatricesFromInputs(); glm::mat4 ProjectionMatrix = getProjectionMatrix(); glm::mat4 ViewMatrix = getViewMatrix(); glm::mat4 ModelMatrix = glm::mat4(1.0); glm::mat4 MVP = ProjectionMatrix*ViewMatrix*ModelMatrix; //transformation을 현재 쉐이더에 보냄 glUniformMatrix4fv(MatrixID, 1, GL_FALSE, &MVP[0][0]); glUniformMatrix4fv(ModelMatrixID, 1, GL_FALSE, &ModelMatrix[0][0]); glUniformMatrix4fv(ViewMatrixID, 1, GL_FALSE, &ViewMatrix[0][0]); glm::vec3 lightPos = glm::vec3(4, 4, 4); glUniform3f(LightID, lightPos.x, lightPos.y, lightPos.z); //텍스처 유닛0에 있는 텍스처를 바인딩한다. glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, Texture); //1st 속성 버퍼 : vertices glUniform1i(TextureID, 0); glEnableVertexAttribArray(0); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer); glVertexAttribPointer( 0, //0번째 속성. 0이 될 특별한 이유는 없지만 쉐이더의 레이아웃과 반드시 맞춰야함 3, //크기(size) GL_FLOAT, //타입(type) GL_FALSE, //정규화(normalized)? 0, //다음 요소까지의 간격(stride) (void*)0 //배열 버퍼의 오프셋(offset) ); //2nd 속성 버퍼 : UVs glEnableVertexAttribArray(1); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, uvbuffer); glVertexAttribPointer( 1, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void*)0 ); //3rd 속성 버퍼 : normals glEnableVertexAttribArray(2); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, normalbuffer); glVertexAttribPointer( 2, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void*)0 ); // Index 버퍼 glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, elementbuffer); // 삼각형 그리기 glDrawElements( GL_TRIANGLES, //mode indices.size(), //count GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, //type (void*)0 //element array buffer offset ); glDisableVertexAttribArray(0); glDisableVertexAttribArray(1); glDisableVertexAttribArray(2); char text[256]; sprintf(text, "%.2f sec", glfwGetTime()); printText2D(text, 10, 500, 60); // Swap buffers glfwSwapBuffers(window); glfwPollEvents(); } // Check if the ESC key was pressed or the window was closed while (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) != GLFW_PRESS && glfwWindowShouldClose(window) == 0); // Cleanup VBO glDeleteBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer); glDeleteBuffers(1, &uvbuffer); glDeleteBuffers(1, &normalbuffer); glDeleteBuffers(1, &elementbuffer); glDeleteProgram(programID); glDeleteTextures(1, &TextureID); glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID); // Close OpenGL window and terminate GLFW glfwTerminate(); return 0; } GLuint LoadShaders(const char * vertex_file_path, const char * fragment_file_path) { //쉐이더 생성 GLuint VertexShaderID = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER); GLuint FragmentShaderID = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER); //버텍스 쉐이더 코드를 파일에서 읽기 std::string VertexShaderCode; std::ifstream VertexShaderStream(vertex_file_path, std::ios::in); if (VertexShaderStream.is_open()) { std::stringstream sstr; sstr << VertexShaderStream.rdbuf(); VertexShaderCode = sstr.str(); VertexShaderStream.close(); } else { printf("파일 %s를 읽을 수 없음. 정확한 디렉토리를 사용 중입니까?\n", vertex_file_path); getchar(); return 0; } //프래그먼트 쉐이더 코드를 파일에서 읽기 std::string FragmentShaderCode; std::ifstream FragmentShaderStream(fragment_file_path, std::ios::in); if (FragmentShaderStream.is_open()) { std::stringstream sstr; sstr << FragmentShaderStream.rdbuf(); FragmentShaderCode = sstr.str(); FragmentShaderStream.close(); } GLint Result = GL_FALSE; int InfoLogLength; //버텍스 쉐이더를 컴파일 printf("Compiling shader : %s\n", vertex_file_path); char const * VertexSourcePointer = VertexShaderCode.c_str(); glShaderSource(VertexShaderID, 1, &VertexSourcePointer, NULL); glCompileShader(VertexShaderID); //버텍스 쉐이더를 검사 glGetShaderiv(VertexShaderID, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &Result); glGetShaderiv(VertexShaderID, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &InfoLogLength); if (InfoLogLength > 0) { std::vector<char> VertexShaderErrorMessage(InfoLogLength + 1); glGetShaderInfoLog(VertexShaderID, InfoLogLength, NULL, &VertexShaderErrorMessage[0]); printf("%s\n", &VertexShaderErrorMessage[0]); } //프래그먼트 쉐이더를 컴파일 printf("Compiling shader : %s", fragment_file_path); char const * FragmentSourcePointer = FragmentShaderCode.c_str(); glShaderSource(FragmentShaderID, 1, &FragmentSourcePointer, NULL); glCompileShader(FragmentShaderID); //프래그먼트 쉐이더를 검사 glGetShaderiv(FragmentShaderID, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &Result); glGetShaderiv(FragmentShaderID, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &InfoLogLength); if (InfoLogLength > 0) { std::vector<char> FragmentShaderErrorMessage(InfoLogLength + 1); glGetShaderInfoLog(FragmentShaderID, InfoLogLength, NULL, &FragmentShaderErrorMessage[0]); printf("%s\n", &FragmentShaderErrorMessage[0]); } //프로그램에 링크 printf("Linking program\n"); GLuint ProgramID = glCreateProgram(); glAttachShader(ProgramID, VertexShaderID); glAttachShader(ProgramID, FragmentShaderID); glLinkProgram(ProgramID); //프로그램 검사 glGetProgramiv(ProgramID, GL_LINK_STATUS, &Result); glGetProgramiv(ProgramID, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &InfoLogLength); if (InfoLogLength > 0) { std::vector<char> ProgramErrorMessage(InfoLogLength + 1); glGetProgramInfoLog(ProgramID, InfoLogLength, NULL, &ProgramErrorMessage[0]); printf("%s\n", &ProgramErrorMessage[0]); } glDetachShader(ProgramID, VertexShaderID); glDetachShader(ProgramID, FragmentShaderID); glDeleteShader(VertexShaderID); glDeleteShader(FragmentShaderID); return ProgramID; } GLuint loadBMP_custom(const char * imagepath) { printf("Reading image %s\n", imagepath); //BMP파일의 헤더에서 데이터를 읽는다 unsigned char header[54]; unsigned int dataPos; unsigned int imageSize; unsigned int width, height; //실제 RGB 데이터 unsigned char * data; //파일을 연다 FILE * file = fopen(imagepath, "rb"); if (!file) { printf("%s는 열수 없다. 경로가 맞는지 확인해라.\n", imagepath); getchar(); return 0; } //헤더를 읽는다, i.e. the 54 first bytes //만약 54 bytes보다 적게 읽혔으면 문제 발생 if (fread(header, 1, 54, file) != 54) { printf("BMP 파일이 아니다\n"); return 0; } //A BMP 파일은 항상 "BM"으로 시작한다. if (header[0] != 'B' || header[1] != 'M') { printf("BMP 파일이 아니다\n"); return 0; } //24pp file임을 확인한다. if (*(int*)&(header[0x1e]) != 0 || *(int*)&(header[0x1C]) != 24) { printf("BMP 파일이 아니다\n"); return 0; } //이미지에 대한 정보를 읽는다. dataPos = *(int*)&(header[0x0A]); imageSize = *(int*)&(header[0x22]); width = *(int*)&(header[0x12]); height = *(int*)&(header[0x16]); //몇몇 BMP 파일들은 포맷이 놓쳐졌다, 놓쳐진 정보를 추측해라 if (imageSize == 0) imageSize = width*height * 3; // 3 : one byte for each Red-Green-Blue component if (dataPos == 0) dataPos = 54; //BMP 헤더는 항상 이 형식 //버퍼를 생성한다 data = new unsigned char[imageSize]; //파일의 버퍼에 있는 실제 데이터를 읽는다 fread(data, 1, imageSize, file); //모든 것은 현재 메모리에 있다, 파일을 닫는다 fclose(file); //openGL 텍스처를 만든다 GLuint textureID; glGenTextures(1, &textureID); //새로이 만들어진 텍스처를 바인딩한다. glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID); //이미지를 OpenGL에게 넘긴다 glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, width, height, 0, GL_BGR, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, data); delete[] data; // trilinear(삼선형) 필터링 glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR); glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR); glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D); return textureID; } GLuint loadDDS(const char * imagepath) { unsigned char header[124]; FILE *fp; //파일을 연다 fp = fopen(imagepath, "rb"); if (fp == NULL) { printf("%s는 열 수 없다. 경로를 확인해라\n", imagepath); getchar(); return 0; } //파일의 타입을 확인한다 char filecode[4]; fread(filecode, 1, 4, fp); if (strncmp(filecode, "DDS ", 4) != 0) { fclose(fp); return 0; } //surface desc를 얻는다 fread(&header, 124, 1, fp); unsigned int height = *(unsigned int*)&(header[8]); unsigned int width = *(unsigned int*)&(header[12]); unsigned int linearSize = *(unsigned int*)&(header[16]); unsigned int mipMapCount = *(unsigned int*)&(header[24]); unsigned int fourCC = *(unsigned int*)&(header[80]); unsigned char * buffer; unsigned int bufsize; bufsize = mipMapCount > 1 ? linearSize * 2 : linearSize; buffer = (unsigned char*)malloc(bufsize * sizeof(unsigned char)); fread(buffer, 1, bufsize, fp); fclose(fp); unsigned int components = (fourCC == FOURCC_DXT1) ? 3 : 4; unsigned int format; switch (fourCC) { case FOURCC_DXT1: format = GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT1_EXT; break; case FOURCC_DXT3: format = GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT3_EXT; break; case FOURCC_DXT5: format = GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT5_EXT; break; default: free(buffer); return 0; } //하나의 OpenGL 텍스처를 생성한다 GLuint textureID; glGenTextures(1, &textureID); //새로이 만들어진 텍스처를 바인딩한다 glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID); glPixelStorei(GL_UNPACK_ALIGNMENT, 1); unsigned int blockSize = (format == GL_COMPRESSED_RGBA_S3TC_DXT1_EXT) ? 8 : 16; unsigned int offset = 0; //밉맵을 불러온다 for (unsigned int level = 0; level < mipMapCount && (width || height); ++level) { unsigned int size = ((width + 3) / 4)*((height + 3) / 4)*blockSize; glCompressedTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, level, format, width, height, 0, size, buffer + offset); offset += size; width /= 2; height /= 2; //Non-Power-Of-Two 텍스처를 사용합니다. //이 코드는 혼란을 줄이기 위해 웹 페이지에는 포함되어 있지 않습니다. if (width < 1)width = 1; if (height < 1) height = 1; } free(buffer); return textureID; } bool loadOBJ( const char * path, std::vector<glm::vec3> & out_vertices, std::vector<glm::vec2> & out_uvs, std::vector<glm::vec3> & out_normals ) { printf("OBJ 파일 로딩중 %s...\n", path); std::vector<unsigned int> vertexIndices, uvIndices, normalIndices; std::vector<glm::vec3> temp_vertices; std::vector <glm::vec2> temp_uvs; std::vector<glm::vec3> temp_normals; FILE * file = fopen(path, "r"); if (file == NULL) { printf("파일 경로를 확인하세요!\n"); getchar(); return false; } while (1) { char lineHeader[128]; //첫번째 라인의 첫번째 단어를 읽는다 int res = fscanf(file, "%s", lineHeader); if (res == EOF) break; //else : 라인의 헤더를 parse if (strcmp(lineHeader, "v") == 0) { glm::vec3 vertex; fscanf(file, "%f %f %f\n", &vertex.x, &vertex.y, &vertex.z); temp_vertices.push_back(vertex); } else if (strcmp(lineHeader, "vt") == 0) { glm::vec2 uv; fscanf(file, "%f %f\n", &uv.x, &uv.y); uv.y = -uv.y; //우리가 DDS texture만을 이용할 것이므로 V의 좌표를 반대로 바꾸어준다. 만약 TGA or BMP 로더를 사용하면 이 것을 제거해라. temp_uvs.push_back(uv); } else if (strcmp(lineHeader, "vn") == 0) { glm::vec3 normal; fscanf(file, "%f %f %f\n", &normal.x, &normal.y, &normal.z); temp_normals.push_back(normal); } else if (strcmp(lineHeader, "f") == 0) { std::string vertex1, vertex2, vertex3; unsigned int vertexIndex[3], uvIndex[3], normalIndex[3]; int matches = fscanf(file,"%d/%d/%d %d/%d/%d %d/%d/%d\n", &vertexIndex[0], &uvIndex[0], &normalIndex[0], &vertexIndex[1], &uvIndex[1], &normalIndex[1], &vertexIndex[2], &uvIndex[2], &normalIndex[2]); if (matches != 9) { printf("파일을 읽을수없다."); return false; } vertexIndices.push_back(vertexIndex[0]); vertexIndices.push_back(vertexIndex[1]); vertexIndices.push_back(vertexIndex[2]); uvIndices.push_back(uvIndex[0]); uvIndices.push_back(uvIndex[1]); uvIndices.push_back(uvIndex[2]); normalIndices.push_back(normalIndex[0]); normalIndices.push_back(normalIndex[1]); normalIndices.push_back(normalIndex[2]); } else { //나머지 라인을 먹는다. char stupidBuffer[1000]; fgets(stupidBuffer, 1000, file); } } //각 삼각형의 각 꼭지점 for (unsigned int i = 0; i < vertexIndices.size(); i++) { //속성의 인덱스를 가져온다 unsigned int vertexIndex = vertexIndices[i]; unsigned int uvIndex = uvIndices[i]; unsigned int normalIndex = normalIndices[i]; //인덱스에서 속성을 가져온다 glm::vec3 vertex = temp_vertices[vertexIndex - 1]; glm::vec2 uv = temp_uvs[uvIndex - 1]; glm::vec3 normal = temp_normals[normalIndex - 1]; //버퍼에 속성을 넣는다 out_vertices.push_back(vertex); out_uvs.push_back(uv); out_normals.push_back(normal); } return true; } void indexVBO( std::vector<glm::vec3> & in_vertices, std::vector<glm::vec2> & in_uvs, std::vector<glm::vec3> & in_normals, std::vector<unsigned short> & out_indices, std::vector<glm::vec3> & out_vertices, std::vector<glm::vec2> & out_uvs, std::vector<glm::vec3> & out_normals ) { std::map<PackedVertex, unsigned short> VertexToOutIndex; //각 input vertex를 위해 for (unsigned int i = 0; i < in_vertices.size(); i++) { PackedVertex packed = { in_vertices[i], in_uvs[i], in_normals[i] }; //out_XXXX에서 비슷한 vertex를 찾는다 unsigned short index; bool found = getSimilarVertexIndex_fast(packed, VertexToOutIndex, index); if (found) { //비슷한 vertex가 VBO에 이미 있다면 대신 사용한다 out_indices.push_back(index); } else { //아니라면 이것은 아웃풋 데이터 추가가 필요하다 out_vertices.push_back(in_vertices[i]); out_uvs.push_back(in_uvs[i]); out_normals.push_back(in_normals[i]); unsigned short newindex = (unsigned short)out_vertices.size() - 1; out_indices.push_back(newindex); VertexToOutIndex[packed] = newindex; } } } void computeMatricesFromInputs() { //glfwGetTime은 한번만 호출된다. static double lastTime = glfwGetTime(); //현재와 마지막 프레임의 시간 차를 계산한다. double currentTime = glfwGetTime(); float deltaTime = float(currentTime - lastTime); //마우스의 위치를 얻는다. double xpos, ypos; glfwGetCursorPos(window, &xpos, &ypos); //다음 프레임의 마우스 위치를 리셋한다. glfwSetCursorPos(window, 1024 / 2, 768 / 2); horizontalAngle += mouseSpeed * float(1024 / 2 - xpos); verticalAngle += mouseSpeed * float(768 / 2 - ypos); //Direction : Spherical 좌표 to Cartesian 좌표 변환 glm::vec3 direction( cos(verticalAngle)*sin(horizontalAngle), sin(verticalAngle), cos(verticalAngle)*cos(horizontalAngle) ); //Right vector glm::vec3 right = glm::vec3( sin(horizontalAngle - 3.14f / 2.0f), 0, cos(horizontalAngle - 3.14f / 2.0f) ); //Up vector glm::vec3 up = glm::cross(right, direction); //앞으로 이동 if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_UP) == GLFW_PRESS) { position += direction*deltaTime*speed; } //뒤로 이동 if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_DOWN) == GLFW_PRESS) { position -= direction*deltaTime*speed; } //오른쪽로 Strafe if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_RIGHT) == GLFW_PRESS) { position += right*deltaTime*speed; } //왼쪽으로 Strafe if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_LEFT) == GLFW_PRESS) { position -= right*deltaTime*speed; } float FoV = initialFoV; ProjectionMatrix = glm::perspective(FoV, 4.0f / 3.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f); ViewMatrix = glm::lookAt( position, //camera here position + direction, //and looks here up // Head is up ); //다음 프레임을 위해 lastTime = currentTime; } void initText2D(const char * texturePath) { //텍스쳐 초기화 Text2DTextureID = loadDDS(texturePath); //VBO 초기화 glGenBuffers(1, &Text2DVertexBufferID); glGenBuffers(1, &Text2DUVBufferID); //Shader 초기화 Text2DShaderID = LoadShaders("TextVertexShader.vertexshader", "TextVertexShader.fragmentshader"); //uniforms' IDs 초기화 Text2DUniformID = glGetUniformLocation(Text2DShaderID, "myTextureSampler"); } void printText2D(const char * text, int x, int y, int size) { unsigned int length = strlen(text); //buffer 채우기 std::vector<glm::vec2> vertices; std::vector<glm::vec2> UVs; for (unsigned int i = 0; i < length; i++) { glm::vec2 vertex_up_left = glm::vec2(x + i*size, y + size); glm::vec2 vertex_up_right = glm::vec2(x + i*size+size, y + size); glm::vec2 vertex_down_right = glm::vec2(x + i*size+size, y); glm::vec2 vertex_down_left = glm::vec2(x + i*size, y); vertices.push_back(vertex_up_left); vertices.push_back(vertex_down_left); vertices.push_back(vertex_up_right); vertices.push_back(vertex_down_right); vertices.push_back(vertex_up_right); vertices.push_back(vertex_down_left); char character = text[i]; float uv_x = (character % 16) / 16.0f; float uv_y = (character / 16) / 16.0f; glm::vec2 uv_up_left = glm::vec2(uv_x, uv_y); glm::vec2 uv_up_right = glm::vec2(uv_x + 1.0f / 16.0f, uv_y); glm::vec2 uv_down_right = glm::vec2(uv_x+1.0f/16.0f, (uv_y+1.0f/16.0f)); glm::vec2 uv_down_left = glm::vec2(uv_x, (uv_y+1.0f/16.0f)); UVs.push_back(uv_up_left); UVs.push_back(uv_down_left); UVs.push_back(uv_up_right); UVs.push_back(uv_down_right); UVs.push_back(uv_up_right); UVs.push_back(uv_down_left); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, Text2DVertexBufferID); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertices.size() * sizeof(glm::vec2), &vertices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, Text2DUVBufferID); glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, UVs.size() * sizeof(glm::vec2), &UVs[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW); // Bind shader glUseProgram(Text2DShaderID); // Bind texture glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0); glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, Text2DTextureID); // Set our "myTextureSampler" sampler to user Texture Unit 0 glUniform1i(Text2DUniformID, 0); // 1rst attribute buffer : vertices glEnableVertexAttribArray(0); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, Text2DVertexBufferID); glVertexAttribPointer(0, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void*)0); // 2nd attribute buffer : UVs glEnableVertexAttribArray(1); glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, Text2DUVBufferID); glVertexAttribPointer(1, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, (void*)0); glEnable(GL_BLEND); glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA); // Draw call glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, vertices.size()); glDisable(GL_BLEND); glDisableVertexAttribArray(0); glDisableVertexAttribArray(1); } } void cleanupText2D() { // Delete buffers glDeleteBuffers(1, &Text2DVertexBufferID); glDeleteBuffers(1, &Text2DUVBufferID); // Delete texture glDeleteTextures(1, &Text2DTextureID); // Delete shader glDeleteProgram(Text2DShaderID); } | cs |
'Game > Graphics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| OpenGL-Tutorial 14 : Render To Texture (0) | 2018.07.01 |
|---|---|
| OpenGL-Tutorial 13 : Normal Mapping (0) | 2018.06.29 |
| OpenGL-Tutorial 11 : 2D Text (0) | 2018.06.28 |
| OpenGL-Tutorial 10 : Transparency (0) | 2018.06.28 |
| OpenGL-Tutorial 9 : VBO Indexing (0) | 2018.06.28 |

